Historic background of pig introduction in Africa
The historical past of pig manufacturing in Africa is a story that spans millennia, deeply intertwined with the continent’s cultural, financial, and agricultural evolution. Home pigs aren’t native to the African continent and have been launched into the continent via acutely aware and unconscious means.
The introduction of pigs in Africa captures 5 important historic occurrences and occasions:
- Early introduction to Northern Africa coast via commerce routes by Phoenicians round 1100BCE.
- European Exploration and Colonization Age: which began from fifteenth century by bringing livestock together with pigs, to supply a well-recognized meals supply and to maintain themselves throughout lengthy sea voyages and in new colonies.
- The Transatlantic Slave Commerce: a interval of pressured motion of tens of millions of Africans to the Americas, which additionally induced merchants to deliver pigs alongside on slave ships as a supply of meals for themselves and the enslaved Africans.
- Actions of Christian Missionaries and settlers who arrived in Africa additionally introduced pigs with them as a part of their efforts to introduce western Agricultural practices in Africa.
- Latest Pig importations, modernization and industrial farming: the importation of pig breeds from different continents, significantly Europe and North America, has contributed to the unfold of pigs in Africa.
Current standing of Africa’s pig trade
1. Present statistics of pig manufacturing in Africa
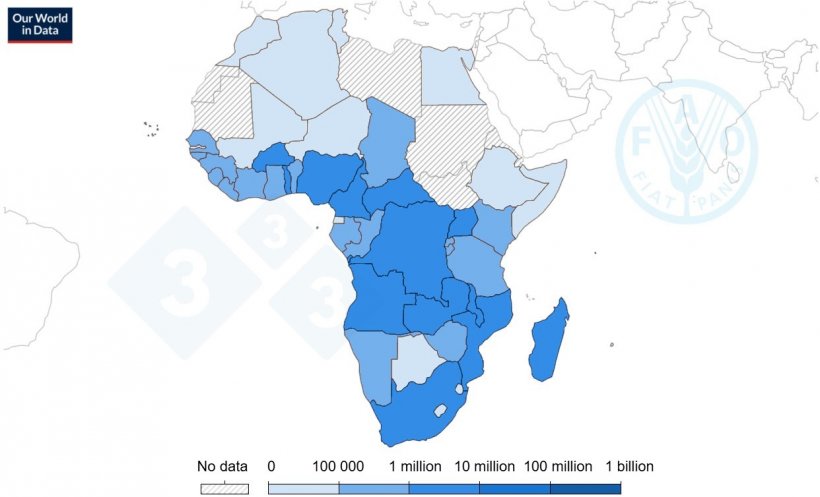
Pig inhabitants in Africa
The full inhabitants of pigs in Africa is roughly 4.6% of complete world inhabitants and within the desk under we are able to see an account of the present distribution between international locations with 1 million to 10 million pigs (FAOSTAT 2023)
| Nation | Estimated pig inhabitants (million heads) |
|---|---|
| Nigeria | 9.51 |
| Malawi | 8.07 |
| Angola | 3.55 |
| Uganda | 2.63 |
| Mozambique | 2.32 |
| Cameroon | 2.18 |
| Burkina Faso | 1.78 |
| Madagascar | 1.75 |
| South Africa | 1.32 |
| Zambia | 1.16 |
| Central African Republic | 1.07 |
| DR Congo | 1.01 |
Pigmeat manufacturing in Africa
The pigmeat manufacturing report of Africa when in comparison with the pig inhabitants displays the impacts of manufacturing techniques in numerous areas.
Pigmeat manufacturing in Africa: Main international locations in pork manufacturing (FAOSTAT 2023)
| International locations | Estimated pigmeat manufacturing (tons) |
|---|---|
| Nigeria | 363,123 |
| South Africa | 351,560 |
| Malawi | 344,550 |
| Burkina Faso | 224,127 |
| Angola | 169,196 |
| Mozambique | 136,637 |
| Uganda | 128,310 |
| Cameroon | 48,560 |
| Tanzania | 44,420 |
| Ghana | 28,820 |
| DR Congo | 27,416 |
| Madagascar | 26,500 |
| Zambia | 24,249 |
| Kenya | 20,460 |
| Senegal | 19,798 |
| Central African Republic | 19,471 |
| Togo | 17,154 |
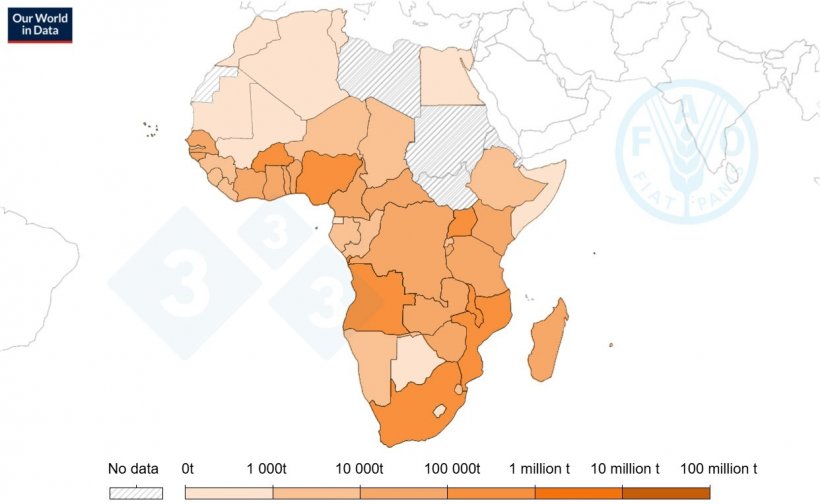
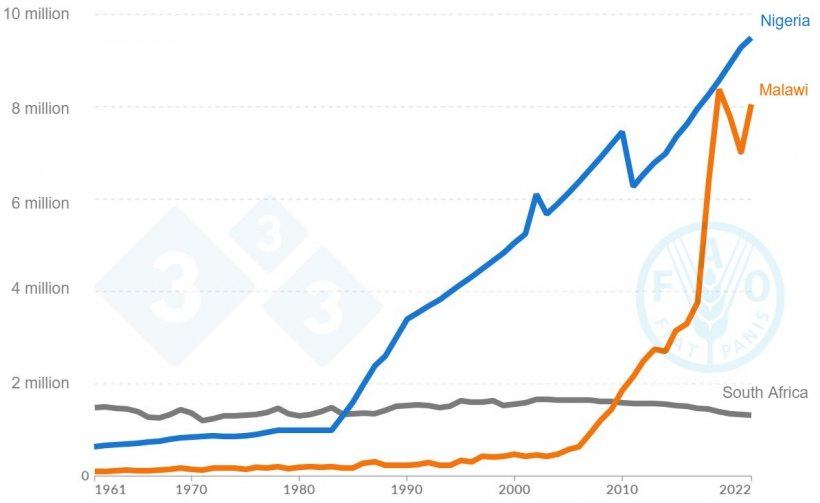
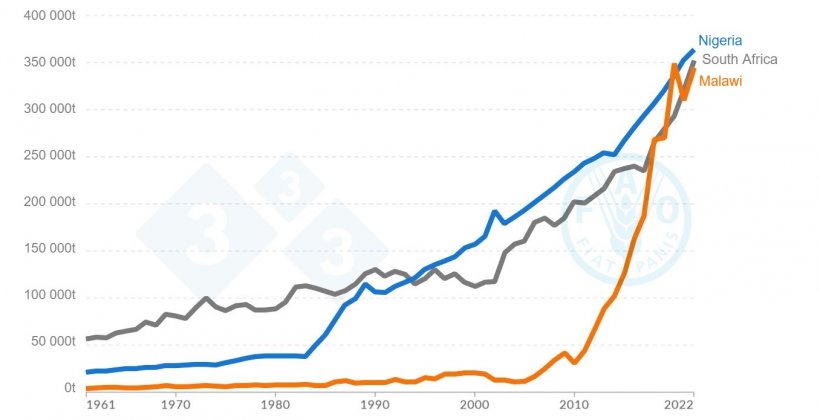
The emergence of South Africa because the second highest pork producer in Africa (regardless of the low inhabitants of pigs within the area) is due to the excessive stage of intensive pig manufacturing system and using high quality genetics within the area.
2. Swine manufacturing techniques in Africa

The present techniques of swine manufacturing within the continent of Africa could be categorised into the next:
- Conventional scavenging system: The place pigs are allowed to roam round to fend for themselves with little or no supplementary feeding. The scavenging system is generally frequent in rural communities and in some peri-urban areas of Africa. Whereas this conventional methodology could seem cost-effective for rural farmers, poses critical challenges that undermine each the profitability and sustainability of pig farming in Africa inflicting unfavourable impacts which poses threats to biosecurity that may embrace illness transmission, public well being danger and as effectively low productiveness.
- The smallholder system: That is often a small-scale subsistence manufacturing the place just a few pigs are raised by particular person households.
- The intensive system: A industrial operation the place massive variety of pigs are confined in managed surroundings on both concrete flooring or deep litter system. Inputs is excessive within the intensive system thus; development price and productiveness is at all times higher.
- Free vary system: In some areas in South Africa, this technique is dominant and distinctive the place pigs are saved in massive camps the place they will roam freely on pasture or grasslands. Free vary pigs forage for a part of their meals and supplemented with extra feed from pure sources.
- The cluster system: Is an organized method the place pig farmers inside a particular geographical space are given entry to a cluster of compartmentalized housings/pens that’s principally owned by the federal government or corporative. The system grants smallholder farmers easy accessibility to some services that enormous scale farmers have however creating the problem of preserve good biosecurity and management illness transmission.
3. Challenges of Africa’s pig trade
The pig trade in Africa holds nice potential as a key driver for meals safety, earnings era, and rural growth. Nonetheless, it faces a number of challenges that hinder its development and sustainability. These challenges embrace:
- Genetic limitations: Conventional African breeds are principally characterised by low productiveness when it comes to development price, feed conversion effectivity, and reproductive efficiency and the entry to industrial breed remains to be restricted and has to extend step by step.
- Lack of rules and insurance policies: Weak or poorly enforced insurance policies and rules have induced a number of detrimental results, impacting numerous sides reminiscent of illness Management, high quality and security requirements, breeding practices, and market costs and market normal amongst others.
- Insufficient infrastructure: In Africa, Pig manufacturing remains to be being affected by lack of recent services, restricted entry to high quality feed and water, poor transportation community, inadequate slaughterhouses and processing services of low high quality.
- Illness challenges (Africa swine fever and different illnesses): African swine fever is probably the most important illness affecting Africa’s pig trade. The fast unfold of the illness is generally brought on by the absence of correct rules and insurance policies that management farms, gross sales and switch of contaminated pigs to slaughterhouses, contaminated meals waste, and actions of scavenging pigs.
- Spiritual and dietary preferences and cultural bias: In lots of African international locations with important Muslim populations, pork consumption is prohibited by Islamic dietary legal guidelines which reduces the market dimension for pork. As well as, in some African cultures, pork just isn’t historically included within the weight-reduction plan, which have result in decrease consumption charges even in areas with out non secular restrictions.
- Lack of technical information and experience: Restricted entry to coaching and technical information about trendy pig farming methods and its adoption have continued to be a problem for small-scale pig farmers, who type the bulk in most international locations. The lack of information, in areas reminiscent of breeding, diet, synthetic insemination, housing, and biosecurity practices has hampered productiveness and restricted the flexibility to undertake improved farming methods, therefore, decreased productiveness and effectivity.
- Market-related points: like excessive value of Feedstuffs, poor unregulated pig costs (principally chased by center offtakers) and restricted entry of farmers to formal markets.
The pig trade in Africa holds substantial prospects and potential for development and growth. By addressing present challenges and leveraging alternatives in home and export markets, technological developments, funding, sustainable practices, and supportive insurance policies, the trade can obtain important enhancements in productiveness, profitability, and sustainability.
With over 1.4 billion folks and projected development to almost 2.5 billion by 2050, the demand for animal protein, together with pork is steadily rising in Africa. All these enhancements will present nice alternatives for the swine trade in Africa.

