Phosphorus (P) is a necessary mineral for bone mineralization, vitality metabolism, and nucleic acid synthesis. In swine diet, it’s the second most considerable mineral after calcium and the associated fee is excessive when included via inorganic sources. Subsequently, utilizing methods to maximise the usage of P current in cereals and legumes utilized in swine diet is of curiosity.
Nonetheless, the bioavailability of plant-derived P is low, since it’s largely within the type of phytate, an insoluble molecule for monogastric animals, which additionally interferes with the digestibility of different vitamins, producing an anti-nutritional impact.
Subsequently, in swine diet, to enhance the utilization of P certain to phytate (phytate P), cut back the anti-nutritional impact of phytate, and cut back the excretion of P to the surroundings – because it has a excessive polluting potential, phytases are used that are exogenous enzymes with phosphomonoesterase exercise able to hydrolyzing the phytic acid molecule and releasing P from phytate.
Why are phytases utilized in swine diet?
First, as a result of 60-80% of the P saved in cereals and legumes is within the type of phytate, i.e., phytic acid salt, a compound with enormously lowered bioavailability in pigs as a result of its insolubility within the gastrointestinal tract and which, as well as, types insoluble compounds with vitamins similar to minerals, proteins, amino acids, and starch that cut back their digestibility (Selle and Ravindran, 2008; Kumar et al., 2012).
Secondly, as a result of the provide of P in swine diets is predicated on the inclusion of sources of inorganic P (Pi) similar to monocalcium phosphate or dicalcium phosphate, primarily. Each are sources obtained from phosphate rock, a finite supply of P. As a result of enhance in demand in sectors outdoors of animal diet, its value is predicted to extend.
Lastly, as a result of the excretion of P not retained by pigs, entails financial losses and in addition has a significant environmental affect as a result of its eutrophying and acidifying motion on the surroundings (Lautrou et al., 2022).
Subsequently, utilizing phytases, enzymes that enhance the bioavailability of P of plant origin, is a dietary technique to cut back P excretion and its environmental affect, cut back dependence on Pi sources, and optimize pigs’ productive efficiency.
Phytic acid, phytins, and phytate
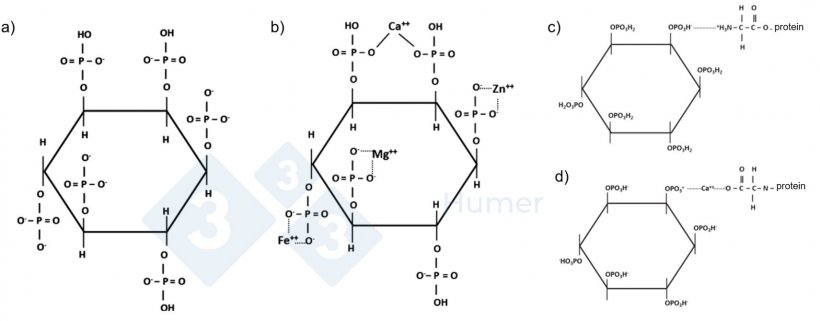
The interchangeable use of the phrases phytate, phytin, IP6 (Inositol Hexaphosphate), and phytic acid is widespread and might trigger confusion. Phytic acid (myo-inositol 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate, IP6, Determine 1a) is the bottom molecule, a extremely negatively charged molecule composed of an inositol ring with six phosphate ester bonds. Its unfavourable cost is dependent upon the pH of the medium, turning into extra reactive at greater pH ranges. When phytic acid binds to minerals similar to iron, zinc, or sodium, it’s known as phytate. In the meantime, when it binds to Ca++, Mg++, or Okay+, it’s known as phytin.
Phytate is the most typical type of P reserve in cereals and legumes. From phytate, crops can launch and make the most of P via their very own phytases, utilizing it in important processes similar to seed germination, photosynthesis, flowering, ripening, root progress, and different capabilities.
In swine diet, the bioavailability of phytic acid for monogastric animals may be very low. Schlemmer et al. (2001) noticed that the solubility of the completely different phytic acid intermediates within the small gut (pH 6.6) was 2% for IP-6, 7% for IP-5, 8% for IP-4, 31% for IP-3, and 75% for IP-2, whereas within the giant gut (pH 6.2), the values had been 2%, 3%, 0%, 6%, and 24%, respectively.
In average pH environments, such because the intestinal surroundings, phytic acid has a powerful unfavourable cost that enables the chelation of cations similar to calcium and sodium, decreasing their bioavailability (Maenz et al., 2001). As well as, phytic acid has been described to inhibit the exercise of Na-Okay-ATPase within the gastrointestinal tract of piglets, a key enzyme in nutrient absorption (Woyengo et al., 2011). It has additionally been proven that phytic acid can bind to proteins over a large pH vary and inhibit the enzymatic exercise of trypsin and α-amylase, which reduces the digestibility of dietary proteins and carbohydrates (Singh et al., 1982; Deshpande et al., 1984). In reality, on the intestinal degree, it could actually kind insoluble protein-mineral-phytate complexes, which hinders its enzymatic hydrolysis and reduces effectivity in the usage of dietary protein (Lopez et al., 2002). Figures 1b-d present completely different complexes that phytic acid can kind by binding with cations or proteins.
Desk 1 exhibits the typical values of the focus of whole P and phytic acid-bound P (phytate P) in elements generally utilized in swine feed. The phytate P content material of cereals ranges between 60 and 80% (of whole P) and in oilseed meals between 60 and 85% (of whole P). You will need to notice that there’s excessive variability in whole P and phytate P content material between completely different batches of elements.
Desk 1. Complete phosphorus (whole P), phosphorus in phytate kind (phytate P), and proportion of phytate phosphorus (phytate P).
| Complete P (g/kg) | Phytate P (g/kg) |
% phytate P
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 2.5 | 2.0 | 80 |
| Wheat | 2.9 | 1.9 | 66 |
| Barley | 3.2 | 2.1 | 66 |
| Rye | 3.0 | 2.0 | 67 |
| Triticale | 3.4 | 2.3 | 68 |
| White sorghum | 2.8 | 1.9 | 68 |
| Wheat bran | 10.0 | 8.3 | 83 |
| Soybean meal (47%) | 6.4 | 4.2 | 66 |
| Rapeseed meal 00 | 11.0 | 8.0 | 73 |
| Sunflower meal, 28% | 9.0 | 7.9 | 88 |
Supply: FEDNA, 03/2025
Phytases: Chemical construction and mechanism of motion
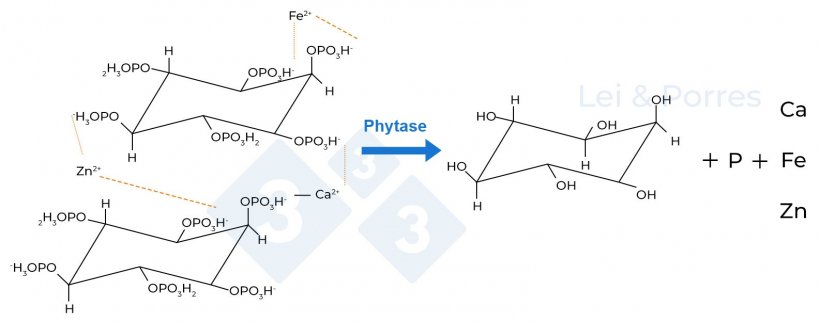
Phytases are enzymes that belong to the subfamily of high-molecular-weight acid phosphatases and catalyze the sequential cleavage of phosphate from phytate on the gastrointestinal degree, changing it into lower-grade inositol phosphate esters (IP5-IP1), Pi, and different components similar to Ca, Fe, and Zn, which can be certain to phytate (Determine 2). That’s, they catalyze the step-by-step removing of P from phytic acid or its salt, phytate, by eliminating the primary P group to acquire a penta-inositol ester (IP5), then the second P to acquire a tetra-inositol ester (IP4), and so forth sequentially. There’s a variety of economic phytases available on the market with various capacities for P launch.
The exercise of phytases is usually expressed in FTU or FYT (Phytase Unit), indicating the quantity of phytase that releases 1 µmol of Pi per minute from 0.0051 mol/L of sodium phytate at a pH of 5.5 and a temperature of 37°C (ISO 30024).
Subsequently, the upper the worth of phytase models, the larger the enzyme’s capacity to degrade phytate and launch P accessible for uptake.
In sensible phrases, every producer supplies the dietary matrix of their phytase, which means technical information sheets that specify the share of whole and digestible phosphorus contributed to the weight-reduction plan, in addition to the availability of calcium, proteins, amino acids, sodium, and vitality, amongst different vitamins, for every focus of phytase used within the ultimate feed (FTU or FYT/kg). Evidently, the weight-reduction plan should comprise ample substrate (phytate P) for the phytase to behave at its most potential.
Since the pig’s pH and digestive capability change because it ages, completely different P and nutrient launch values might be estimated for a similar phytase relying on the pig’s age. It’s price highlighting the next device (obtain in Excel format) developed by Kansas State College, which permits us to calculate the dosage of various business phytases and the quantity of P launched in swine diets.
The impact of phytases on the discharge of Pi from diets is dependent upon a number of elements, such because the focus and supply of phytate within the weight-reduction plan, the pig’s age, the focus and supply of minerals, and the supply and dosage of phytase within the weight-reduction plan. On this regard, copper (Cu) supplementation can affect phytase exercise and the solubility of phytate P. Research in poultry have proven that prime dietary Cu ranges can cut back the solubility of phytate P and reduce its hydrolysis by phytases at pH 4.5 and 6.5 (Hamdi et al., 2017). Moreover, the kind of Cu supply used can have an effect on these outcomes, as copper sulfate (CuSO₄) has been proven to cut back phytate P solubility greater than dicopper oxide (Cu₂O) (Hamdi et al., 2017).
Varieties of phytases
Phytases might be categorized based mostly on their manufacturing supply (yeasts, micro organism, and fungi), the place on the phytate molecule the place hydrolysis begins (3-phytases and 6-phytases), and their optimum pH for exercise (alkaline and acidic).
Microbial phytase is essentially the most generally used phytase in swine diet, produced by yeasts, micro organism, and fungi. Within the European swine market, phytases can be found from fungi similar to Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus oryzae, and Trichoderma reesei, in addition to from E. coli micro organism, amongst others. To boost phytase efficiency and manufacturing, particular modifications have been made to producer strains in latest many years. These enhancements have elevated the effectivity, exercise, and thermostability of phytases. In reality, most phytases available on the market are thermostable on the temperatures reached through the technological pelleting course of.
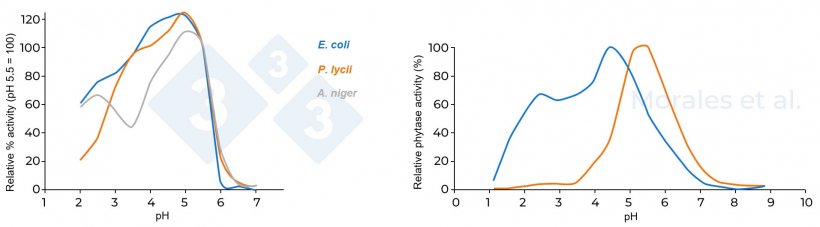
Microbial and fungal phytases can preserve a superb degree of exercise after extended thermal publicity and underneath a large pH vary. In reality, phytases of bacterial origin are secure even at pH values above 8.0 and beneath 3.0 (Greiner and Konitzny, 2006). Determine 3 exhibits the distinction within the relative exercise of various sources of phytases in accordance with pH.
However, phytases might be categorized into two classes based mostly on the place hydrolysis begins on phytate: 3-phytase (EC 3.1.3.8) and 6-phytase (EC 3.1.3.26). The previous releases the primary phosphate group on the C3 place of the myo-inositol hexaphosphate ring and is generally of microbial origin, whereas the latter releases the primary phosphate group on the C6 place and is primarily remoted from crops. Nonetheless, there are exceptions, similar to E. coli phytases, that are 6-phytases. In swine diet, most phytases accessible in Europe belong to the 6-phytase group.
Latest findings
1. The impact of lowered feed pH, phytase addition and their interplay on mineral utilization in pigs.
The target of the research was to judge the impact of decreasing feed pH via the inclusion of 14 g/kg of formic acid, in addition to the inclusion of phytase and their interplay, on productive efficiency, mineral retention, and bone mineralization in a 2×2 factorial design in pigs weighing 20 to 30 kg BW.
No interplay was noticed between formic acid and phytase inclusion for any of the analyzed parameters. Nonetheless, phytase inclusion elevated progress, P and Ca digestibility, and bone mineralization. In the meantime, formic acid inclusion improved progress, feed conversion, and the digestibility of Mg, Fe, and Ca.
In conclusion, the research confirmed the advance in P digestibility with phytase inclusion however didn’t observe an enhancement in phytase exercise with formic acid inclusion.
2. Obvious digestibility of vitality and vitamins and effectivity of microbial phytase is influenced by physique weight of pigs.
The target of the research was to judge whether or not growing dietary phytase ranges leads to larger phytate degradation and improved digestibility of minerals, amino acids, and vitality, whatever the pig’s physique weight. A complete of 18 pigs geared up with a T-cannula on the distal ileum had been analyzed from 25 to 125 kg BW and assigned to 6 diets containing 0, 250, 500, 1,000, 2,000, or 4,000 FTU/kg.
The outcomes confirmed that, whatever the pig’s physique weight, growing phytase inclusion improved the obvious ileal digestibility of crude protein and most amino acids, in addition to the obvious whole tract digestibility of Ca, P, Okay, Mg, and Na. Nonetheless, the findings point out that the effectivity of dietary phytase in degrading phytate seems to lower as pigs age.
3. Rising pigs’ diets with elevated phytase exercise and lowered accessible phosphorus resulted in comparable efficiency and environmental impacts.
The target of the research was to judge the environmental affect and productive efficiency of castrated pigs (15 to 30 kg BW) fed diets with lowered accessible phosphorus ranges and elevated phytase inclusion (0, 250, 500, 750, and 1,000 FTU/kg).
The outcomes present that utilizing greater ranges of phytase could be a dietary technique to partially cut back the usage of phosphate sources, similar to dicalcium phosphate on this case, whereas sustaining animal efficiency and decreasing nitrogen and phosphorus excretion into the surroundings. Nonetheless, when it comes to environmental affect (carbon footprint, acidification, eutrophication, vitality demand, terrestrial ecotoxicity, and land use), no important variations had been noticed between the evaluated therapies.

