There are two principal methods for chook feathers to be colourful. One is predicated on pigments, one on construction.
With some justification, it may be mentioned that the latter just isn’t actually chemistry however quite physics. So, I’ll give attention to pigment-based coloration, but additionally need to briefly clarify structural coloration first.
Structural coloration in chook feathers comes from the bodily interplay of sunshine with nanostructures within the feathers and their elements (primarily keratin, melanin, and air), not from pigments. Totally different mechanisms create robust and infrequently iridescent colours:
- Skinny-film interference occurs when layers of supplies with totally different refractive indices (e.g., keratin and air) mirror gentle. Some wavelengths then reinforce one another whereas others cancel one another out. This leads to shiny colours that change with the viewing angle. The altering colours of a hummingbird’s or sunbird’s throat are an instance.
- Coherent scattering occurs when nanostructures (for instance, air-filled holes in keratin) scatter gentle in-phase, in order that solely sure wavelengths are amplified. This leads to matte however vivid colours, usually blues and greens, for instance, within the blue of a Blue Jay.
- Extremely ordered nanostructures act like photonic crystals, reflecting particular wavelengths, which ends up in exact angle-dependent colours. Starlings are an excellent instance.
These structural colours will be extra intense and sturdy than pigments, and also can change because the construction of the feathers adjustments (consider the Starling’s feathers solely getting its shiny colours as soon as these begin carrying down). Moreover, they are often more cost effective from an power standpoint, as they don’t require the manufacturing or assortment of any particular extra chemical substances.
Nonetheless, solely about 20-30% (although this can be a tough estimate) of feather colours are purely structural. One other 10-20% are blended (for instance, inexperienced feathers as the results of blue structural coloring and yellow pigment), whereas the bulk (possibly 60-70%) of colours are pigment-based.
Pigment-based shade means the colour comes from the person molecules absorbing some gentle wavelengths. So, the colour ensuing from this absorption is dependent upon the person molecule – and right here, we’re clearly within the realms of chemistry.
4 teams of pigments are considerably widespread in chook feathers, beginning with the commonest and ending with the least widespread:
- Melanins: blacks, browns, grays
- Carotenoids: reds, oranges, yellows
- Porphyrins: reddish-browns, fluorescent pinks/greens below UV
- Psittacofulvins (in parrots): pink/yellow pigments
How about their chemistry?
Melanins (sure, there are a number of of them – nothing is ever easy) are produced by birds internally through the oxidation and subsequent polymerization of tyrosine, an amino acid. The ensuing polymers are insoluble in water and most solvents, have variations of their construction (which means they are often considerably undefined), and have fragrant rings with delocalized electrons, which makes them good at absorbing totally different wavelengths and thus provides them their darkish shade.
An Eumelanin construction
The truth that these melanins will be produced from supplies already accessible to birds through their regular vitamin makes them comparatively low cost energetically. One other benefit is that melanins additionally stiffen feathers, make them extra abrasion-resistant, and extra immune to micro organism.
So, that makes melanins very helpful pigments – however their shade vary is restricted, and their relative ease of manufacturing makes them much less appropriate as expressions of excellent well being (necessary to find a mate). Carotenoids are significantly better suited to this perform.
Beta-Carotin
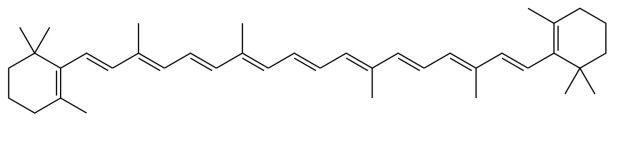
Carotenoids are far more expensive for birds to accumulate, as they can not synthesize them internally however must get them from bugs, fruits, or crops. For instance, Widespread Inexperienced Magpies could flip blue (from inexperienced) if missing carotenoids in captivity.
As well as, carotenoids produce other helpful features for birds, strengthening their immune techniques and functioning as antioxidants. So, exhibiting the colour of carotenoids in its plumage is a method for a chook to showcase its excessive degree of assets.
All carotenoids are tetraterpene derivatives, so that they comprise 40 carbon atoms and are based mostly on 8 isoprene models. They’re extremely unsaturated with conjugated double bonds, enabling them to soak up gentle of various wavelengths (usually 400 to 550 nm, or violet to inexperienced gentle, leading to yellow, orange, or pink shade) relying on the detailed chemical construction.
Some carotenoids are utilized immediately as pigments by birds; others are first transformed into totally different, however nonetheless associated chemical compounds with totally different colours and properties.
Porphyrins are a lot rarer pigments in birds than melanins and carotenoids. Chemically, they’re natural compounds based mostly on a cyclic tetrapyrrole: 4 pyrrole rings related in a hoop, forming a steady fragrant system.
Primary Porphyrin construction
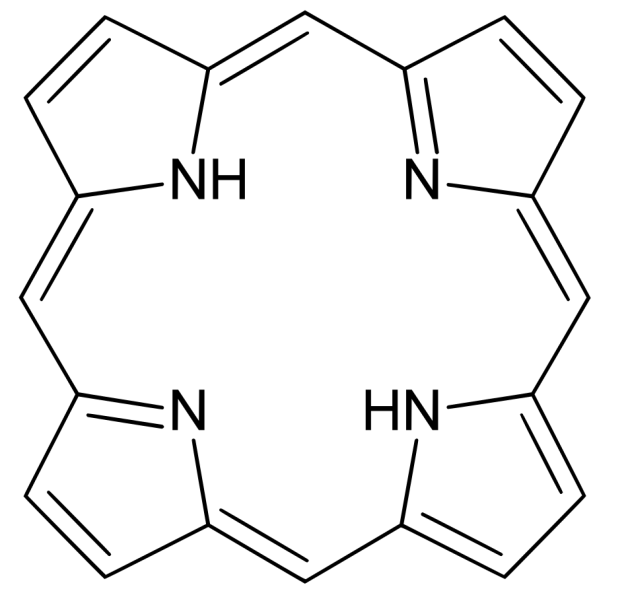
Birds can synthesize porphyrins themselves. They use them to attain colours together with pink, brown, inexperienced, and pink. Some porphyrin colours fluoresce below UV gentle (which is invisible to people however seen to some birds). One other attention-grabbing side is that these colours should not very steady below direct daylight, limiting their use to areas reminiscent of underwings.
Lastly, psittacofulvins will be regarded as the reply of the parrot household to carotenoids – psittacofulvins have related colours (pink, orange, yellow) however are solely utilized by true parrots, and have a very totally different chemical construction. They’re linear polyenes terminated by an aldehyde group, with the size of the polyene chain because the distinction between the person psittacofulvins. These pigments are produced by the parrots of their rising feathers.
Generic components of Psittafulvin
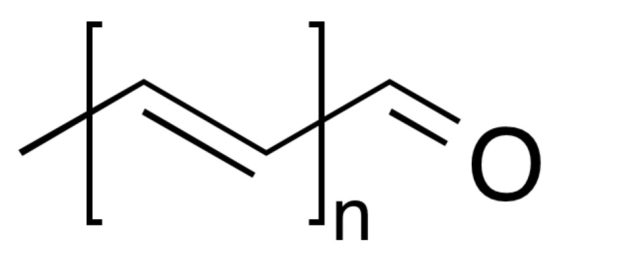
Many birds use each structural and pigment-based coloration on the identical time. For instance, in parrots, the blues and greens are structural whereas the reds and yellows are based mostly on the pigment class simply talked about, the psittacofulvins.
Supply:
Picture: Widespread Inexperienced Mapgie, Hongbenghe, Yunnan, December 2023

